There are different types of 3D printing methods. We have mostly been featuring FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printing, a method that involves material extrusion. You are well familiar with how it works: it extrudes the melted filament from its hotend, creating the print layer by layer.
On the other hand, DLP printing works in a completely different way. Learn more about DLP printing and how it can produce prints with a smoother finish and higher resolution at a much faster rate.
What is DLP Printing?
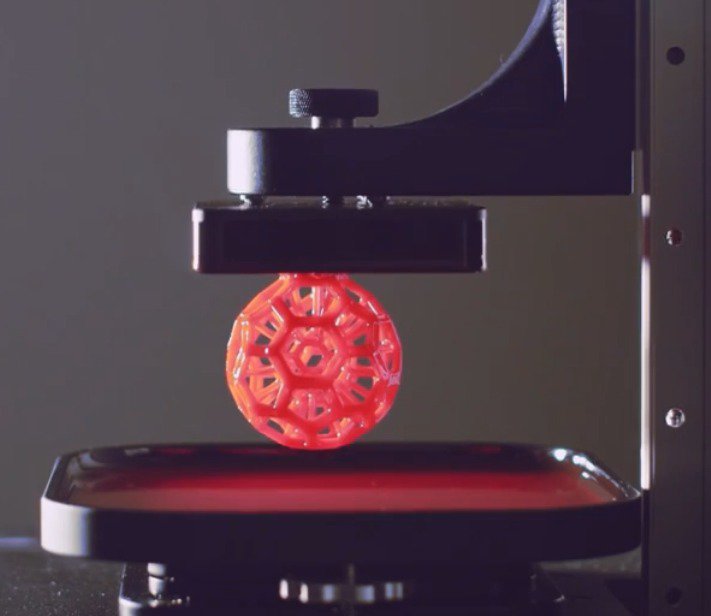
DLP (Digital Light Processing) printing is a form of vat polymerization. It requires a liquid photopolymer resin material that can solidify into different patterns under a light source while its build plate moves up and down incrementally. Its process makes printing faster since a whole layer can be solidified simultaneously, thanks to the light source it uses called digital light projector screen technology.
The projector works together with a digital micromirror device (DMD). It contains up to millions of small micromirrors that direct the light that creates the pattern of a layer on the bottom of the resin tank. The resolution of an object depends on the number of micromirrors of the DMD.
DLP Printing: Advantages & Disadvantages over FDM Printing
Advantages:
- Smooth finish: DLP printers have a small minimum feature size that allows them to create parts with a smoother finish. With FDM printers, you have to use special filament blends or do post-processing to get smooth prints.
- High resolution: DLP printing is only limited by the micromirrors that its DMD is equipped with. The more micromirrors your printer has, the better the resolution your object will have. If you want to create incredibly detailed and intricate objects, DLP printing is your best bet.
- Faster printing speed: Each layer can be solidified in one go with DLP printing. FDM 3D printers have to extrude melted material to build each layer upon layer, going from one end to another.
Disadvantages:
- Brittle parts: If you’re creating structural or functional components that require strength, then DLP printing is not for you. DLP-printed parts are brittle.
- Complicated to use: There are far too many different processes and starting materials involved with DLP printing. Meanwhile, FDM printers are easier to set-up and start printing with.
-
More expensive to use: There are many materials to use and there are limited suppliers of resins in the country so there isn’t a lot of choices.
h2. DLP Printing materials
Resin Materials
Monocure Rapid Resin

The Monocure Rapid Resin range is designed for low-powered LED DLP type printers. The cure speed is up to 4 X faster than the standard resin.
Monocure Rapid Flex

The FLEX100™ has an extremely high level of flexibility for compressible and bendable 3D-printed models.
Resin Cleaners

Resin can get messy. RESINAWAY® cleaner is chemically engineered to quickly and effectively remove uncured UV photopolymer resin from printed parts, build plates, vats, and instruments.
FEP Sheets

FEP sheets are designed as the release layer for UV 3D printer resin vats.
Get more detailed and high-resolution 3D prints with DLP printing!
If you want intricately designed prints that are made for decorative purposes, it’s time to start DLP printing! Our range of resin materials is growing! Keep your eyes peeled for more news about our expanding resin range in the coming weeks. For inquiries about DLP printing and its materials, you can call us by phone or email.